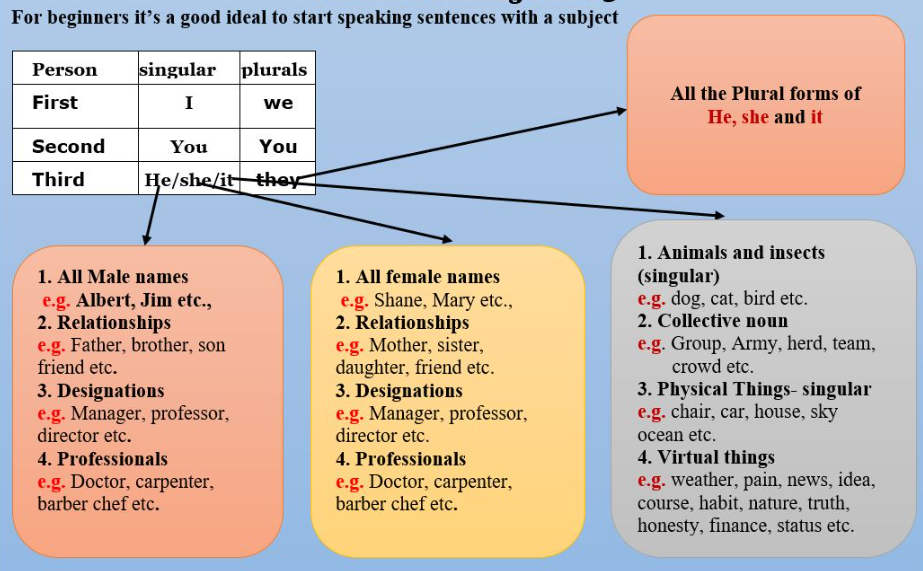
The First step in making a sentence is to understand the concept of the first, second and third person.
CONCEPT OF FIRST SECOND AND THIRD PERSON
First-person refers to the person who speaks to someone. The second person refers to the listener. Third
person refers to the person or thing, which the first and second person talk about. The term ‘person’ includes non-living things too.
| Person | singular | plurals |
| First | I | we |
| Second | You | You |
| Third | He/she/it | they |
Concept of a Subject
When we speak or write, we always speak about some person or thing. The person or thing we speak about is called the subject. Generally, the subject comes first in a sentence. Every sentence needs a subject. If you don’t have a subject, then the sentence is incorrect and nobody will understand what you are talking about.
Note: The subject is not always required. Verbally, the person listening to you will understand what you are talking about. For example:
Want some water? = Do you want some water? And also a word or two can also mean a sentence, for example: me too = do you need me too. ‘Yes’ or ‘no’ also a single word sentences, where the subject is understood.
Bill is a student.
The plane arrived late.
The old building is a museum.
These four books are mine.
The climate of Alaska is very cool.
The president of India is coming today.
The Chinese team played well.
Students are busy.
Jim and Shane came late to the class.
The subject can be a noun, pronoun, collective noun, adjective or phrase, also the subject can be a single word or a group of words
In the above sentences Bill, the plane, the old building, these four books, the climate of Alaska, The president of the USA, the Chinese team, students, Jim and Shane called subjects. You would have seen that some subjects are just a ‘word’ and other subjects consist of a group of words called noun-phrase
Note: A noun that consists of a group of words is called a noun phrase. e.g. The President of the USA, a cup of silver
NOTE: 1. In imperative sentences (command/request), the subject is left out
For Example: Come here. , Sit down etc. You come here. You sit down.
2. ‘It’ and ‘There ‘are’ called dummy subjects. They are used at the start of a sentences which do not have subjects of their own. They are used to balance sentences (we shall see it later)
3. All the subjects have their PRONOUNS.
Conversion of the subject to subject-pronoun
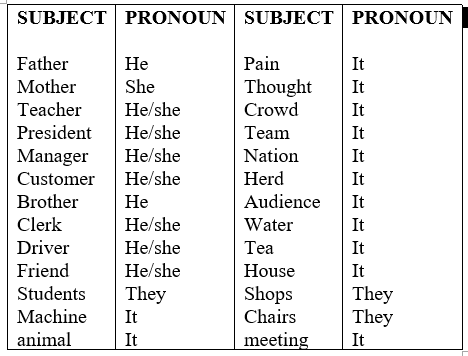
Why do we need to learn the conversion of subject to subject-pronoun?
The subject list is endless, It would be a good idea to just remember subject pronouns because they are limited, besides it’s easier to make sentences with the subject pronouns (or just pronoun) than the actual subject. The following table displays the pronouns of all the subjects (Things people animals, virtual things etc.)
SUBJECT PRONOUN (We will refer to subject-pronoun as just subject in future.)
Object in a Sentence
Object refers to the part of a sentence that is affected by the subject
The boy hit the ball ( The effect of the subject ‘boy’ is on the ball so the ball is the object)
We bought a house ( The effect of the subject ‘we’ is on the house so the house is the object)
Rachel gave a book to Bill (the effect of the subject ‘ Rachel’ is on Bill so Bill is the object)
Conversion of an object to object-pronoun
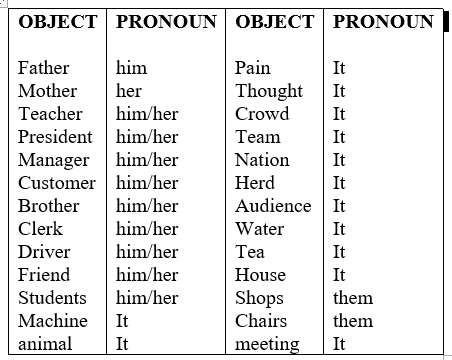
Why do we need to learn the conversion of an object to object-pronoun?
The Objects list is also endless, It would be a good idea to just remember object-pronoun because they are limited, besides it is easier to make sentences with the Object pronouns than the actual objects. The following table displays the pronouns of all the Objects (Things/virtual things people animals etc.), that exist in the world.
OBJECT PRONOUN OR OBJECT
| Person | Singular | Plural |
| First | Me | Us |
| Second | You | You |
| Third | Him/Her/It | Them |
Making Sentences with Subject and Object Format
| Subject Pronoun Singular | Object pronoun Singular | Subject Pronoun Plural | Object Pronoun Plural |
| I | me | we | us |
| you | you | you | you |
| he | him | they | them |
| She | her | they | them |
| it | it | they | them |
| Who | whom | Who | whom |
NOTE: There is no plural form for you
Generally, a subject comes first in a sentence and an object comes at the end. A sentence may contain more than one object, Let’s see some examples:
Samul gave a book to John. (Noun form)
He gave a book to him. (pronoun form)
Sarah and Bill gave keys to Jim. (Noun form)
They gave keys to him. (Pronoun form)
Elizabeth called Sarah (Noun form)
She called her. (Pronoun form)
Albert invited John and Jim. (Noun form)
He invited them. (Pronoun form)
Use the above table to make simple sentences using the pronouns
I gave you
She gave them
They gave us
He gave him
I saw them
We called her
NOTE: In Phrases, proverbs, and Idioms grammar rule is not followed
Making Sentences with Possessive Pronouns
Possessive means ownership of things over which we or someone else has control, For example:
Possessive Pronoun Table
| Singular | Plural |
| My/mine | Our/ours |
| Your/yours | Your/yours |
| his | Their/theirs |
| Her/hers | Their/theirs |
| its | Their/theirs |
This is my book. = This book is mine, not yours.
That is Her box. = That box is hers, not mine.
This is Their house. = This house is theirs, not ours.
This is Our college. = This college is ours, not yours.
Making Sentences with Reflexive Pronouns
Reflexive Pronoun table
| Singular | Reflexive | Plural | Reflexive |
| I | myself | we | ourselves |
| you | yourself | you | yourselves |
| He | himself | They | Themselves |
| She | herself | They | Themselves |
| It | Itself | They | Themselves |
He himself painted the house. (Because he couldn’t get a painter)
She herself finished the work (Though she needed others’ help)
Students themselves learned the lesson (The teacher was absent)
What is a predicate?
A Predicate in a sentence is the part of the sentence, that informs the person what the subject is, what the subject is doing or the state/condition of the subject, the verb is always In the predicate part, let’s see some examples:
I am hungry./My brother is an intelligent boy./This machine is costly./We are going to a movie theatre now./That building is very strong.
NOTE: The lesson is related to ‘Science of sentence making 2, lesson 2’


